Requirements Management Plan
What is a Requirements Management Planning Software?
The purpose of a Requirements Management Planning software is to keep track of important, necessary information required to manage a project efficiently. Requirements Management is a set of activities that ensure the documentation, elicitation, refinement and any changes towards the requirements are met and dealt with accordingly to the customer’s satisfaction. When managing through a software application, requirements can be linked to test data, risks, safety and any other critical issues.
A requirement is any feature of a project that the deliverable must present. To better ensure these requirements are met, a project manager should utilize a Requirements Management Planning software to better keep track of and input data. To begin this process, one must define all needed requirements, input the requirements and then why they are needed. The requirements plan is then reviewed and the most important requirements are prioritized first.
Priorities of a Requirements Management Plan
Typically there are three to four priorities within the Requirements Management Plan. An Introduction begins the plan, where the project and requirements are defined and it’s made clear why they should be managed. Provide a brief description of the purpose of the project to be communicated to anyone who hasn’t seen your project charter.
Next, you will provide an overview of the required management process and who is responsible for completing activities and processing workflows for requirements. You will also include information on tools, reporting, processes and procedures needed to complete the requirements detailed in the project.
Next, The Requirements Management Plan should include defined requirements that will be managed, traced, change management, workflow and activities. Traceability is essential as it allows one to see the associations between requirements, design, verification plans, test and results.
Lastly, if there are changes to any requirements. There should be a direct process that manages any changes to the requirements or project overall. The change process, whether a formal scope or specific change control process, should be detailed here as well.
Purpose of Managing Requirements through Software
Not only does managing requirements through a software application increase the organization of the project, it also helps reduce costs, improves quality of requirements, decreases time taken, decreases risks, and enables effective scope management. According to studies shown, a Requirements Management Plan improves all major aspects of an organizational strategy.
In 2004 CHAOS reported that 44% of projects were challenged, meaning they were either late, over budget and/or the requirements did not meet expectations. 24% of projects failed, meaning they were canceled prior to completion, or delivered and never used. A Requirements Management Planning software can help to keep day-to-day business, portfolios, projects and programs organized and on track.
When do you need Requirements Management Planning Software?
Put simply, always. There is probably never a time when a Requirements Management Planning software will not be beneficial to a project or program. You can start managing requirements at any time, it is never too late to develop a plan. Ideally, you should be managing requirements from the initial strategic plan, to the execution phase of the process. No matter the complexity of the project at hand, it is always beneficial to implement a Requirements Management Planning software.
Requirements Management Plan Process
With each plan comes a very specific and important process that should be strictly followed. This process pulls together all of the steps mentioned above.
- Identify stakeholders
- Gather all requirements
- Analyze requirements
- Document requirements
- Prioritize requirements (must be agreed and signed off on)
- Communicate requirements.
- Monitor/track requirements
- Manage any changes to requirements
- Final requests report
Requirements Attributes
Each requirement needs its own unique identifier and name. Below are the attributes that should be captured for each requirement:
- Unique requirement identifier
- Name
- Description
- Version number
- Type
- Change History
- Status
- Priority level
- Owner responsible
- Trace information
- Process/Activity reference
- Not to mention the actual requirement text
Traceability
Traceability is one of the most important components of a requirements management plan. This chart helps to understand why the requirements need to be traced, if the requirements have been met, prioritize requests and trace the impact of change. To the right is a chart from pmi.org where you can see the flow from business requirements outcomes/goals all the way to testing scenarios and cases.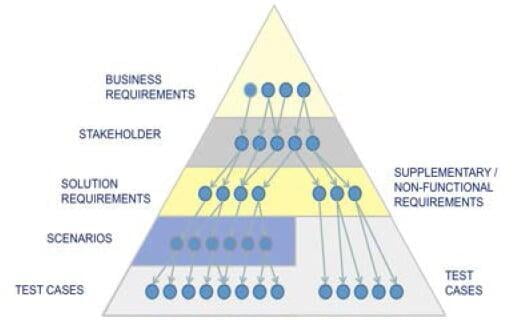

Why is Requirements Versioning Important?
This is the process of tracking the history of all changes made to a specific requirement. That way no one is looking at an older version of a requirement that has needed changing. It is important for everyone working on the project to be made aware of requirements changes to defer from lost time or extra expenses. Some of the more important requirements could change a number of times. With a well maintained history of these changes, you can ensure the project remains on schedule and no confusion is presented to project managers.
Tips for Success
- Implement the Requirements Management Planning software at the start of the project and incorporate it throughout the entire project’s lifecycle.
- Customers, Stakeholders, developers and managers should all be involved in the requirements management plan.
- Communicate to all team members the importance of adhering to the requirements management plan.
- Communicate with team members when gathering, documenting and verifying all requirements or change to requirements.
- A Requirements Management Tool should be used to show consistency and traceability, as well as assist in the verification, validation, and testing of the requirements.
- Implement a requirements configuration management process to ensure that no changes are made to the baseline requirements without first performing a risk analysis, re-estimate impacts to costs and time schedule and receive validation from stakeholders.

